
DS001 Monocot & Dicot Roots, cs Valley Microscope
Anatomy of Monocot Root. Monocot and Dicot Roots: Type # 1. Anatomy of Dicotyledonous Roots: I. Cicer- Root: ADVERTISEMENTS: It is circular in outline (Fig. 170) and reveals following tissues from outside with-in: Epiblema: 1. It is the outermost layer consisting of many thin-walled cells. 2. From some of its cells arise unicellular hair.
Monocot Stem Cross Section. Lm Photograph by Science Stock Photography
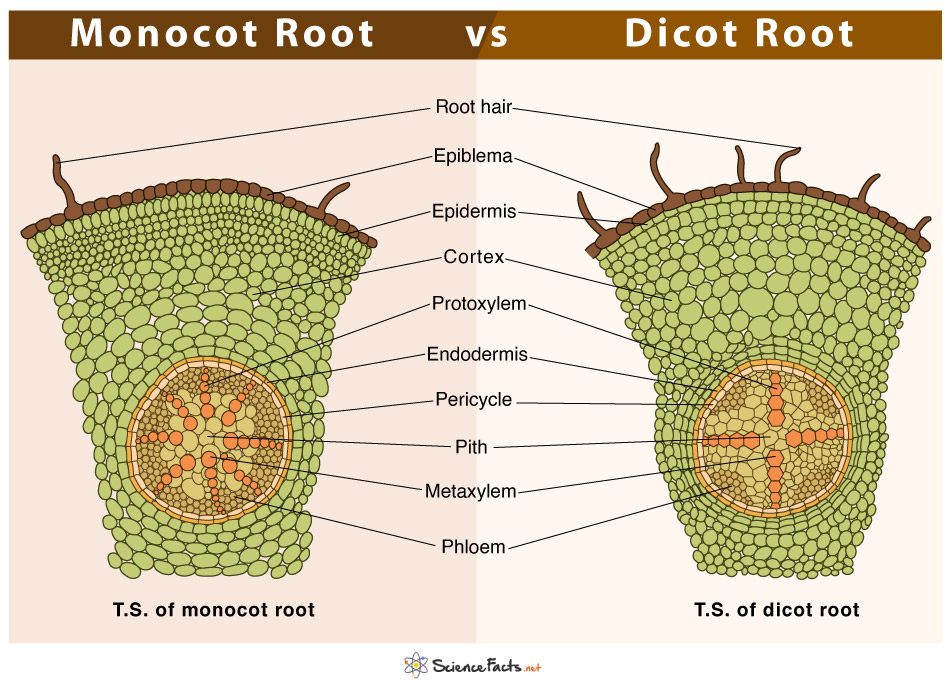
Monocot Root These plant roots have a comparatively wider, and fibrous root-like structure. Dicot Root These plant roots have a comparatively narrow, and tap root-like structure. Normally, dicots and monocots differ in four aspects which include stems, flowers, leaves, and roots.

SOLUTION Anatomy of monocot root Studypool
Monocots, as the name implies, are defined by having seeds that contain a single (mono-) embryonic leaf known as a cotyledon. This is a monophyletic group that constitutes a majority of our agricultural biomass and include many important crop staples including, but not limited to, rice, wheat, corn, sugar cane, bamboo, onion, and garlic.

Monocot & Dicot Root Prepared Microscope Slide 75x25mm — Eisco Labs
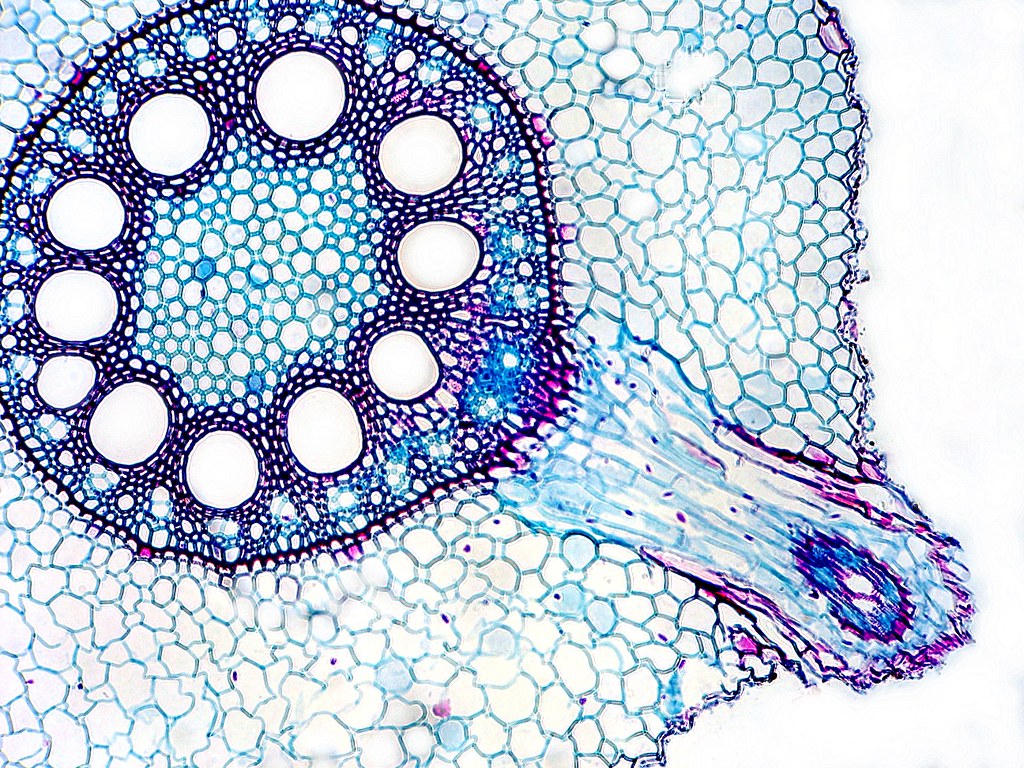
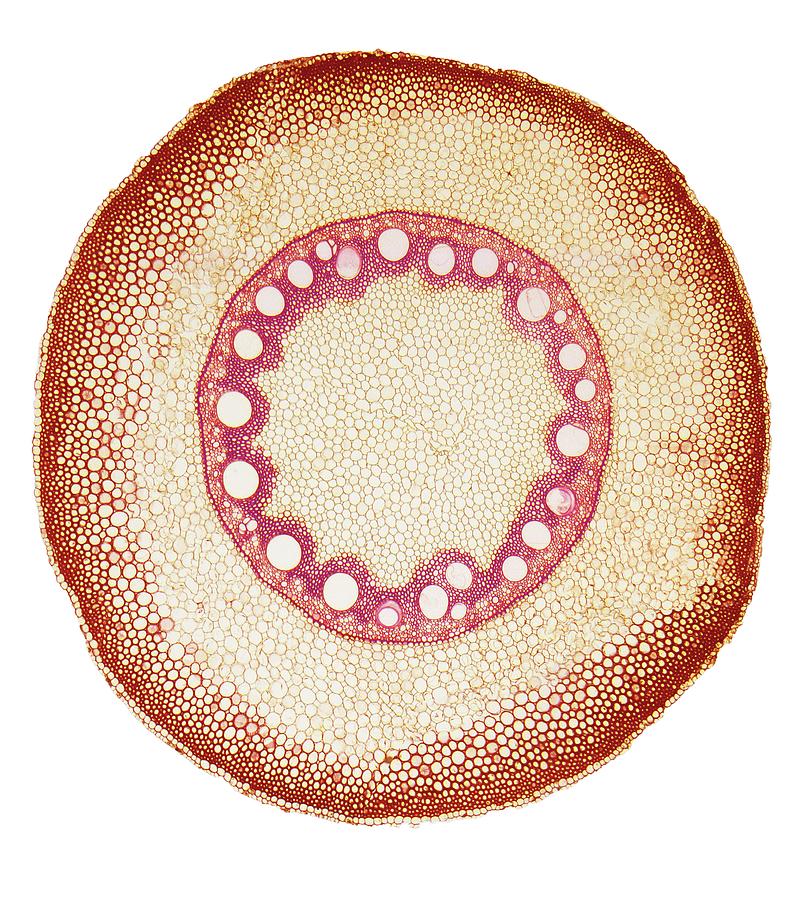
Most of the root is composed of cortex tissue, and the endodermis, the innermost layer of the cortex, borders the stele. The outer layer of the root (external to the cortex) is the epidermis. Figure 3.2.3. 4: Eudicot root cross section. From center out, the xylem (in red) make an X, and the side tissues (green) make up the phloem..
Monocot Stem Cross Section Monocot Root Cross Section Structure (with
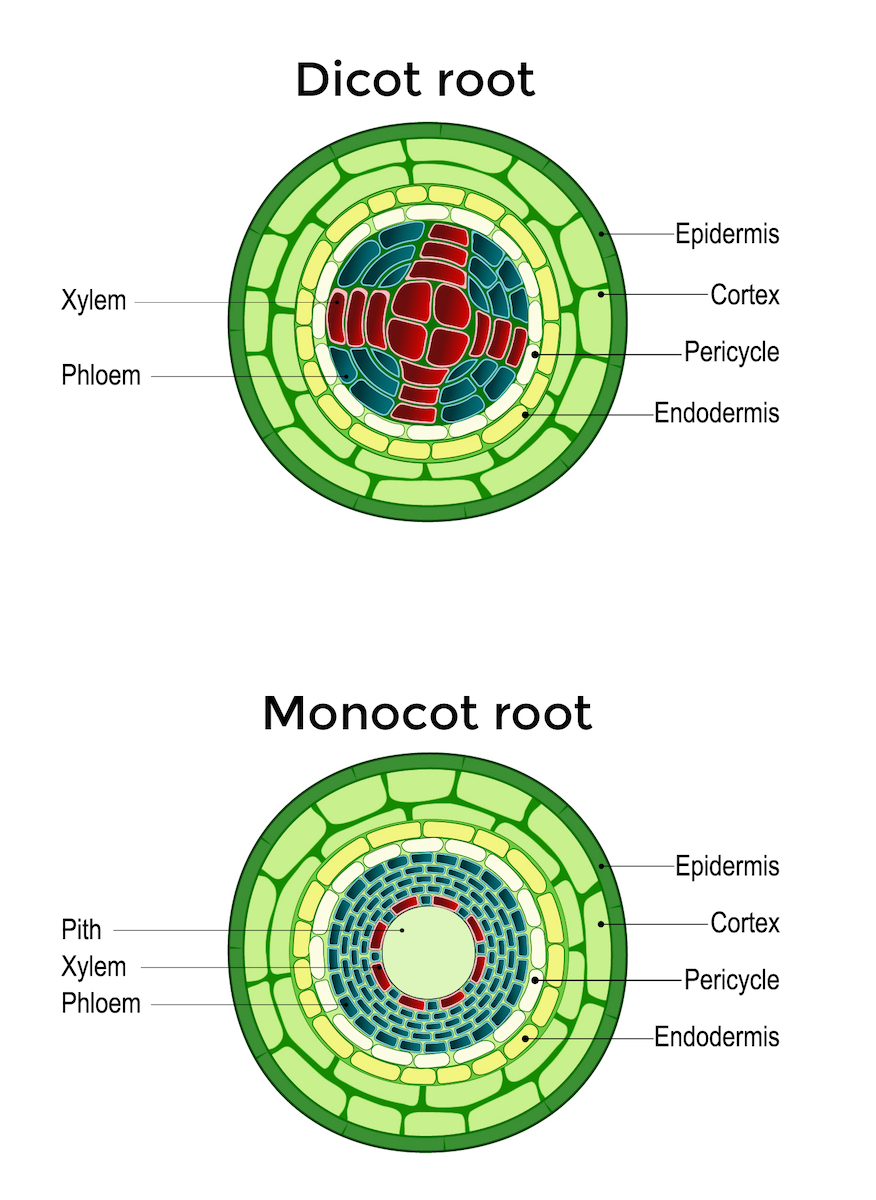
Root systems are mainly of two types (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Dicots have a tap root system, while monocots have a fibrous root system. A tap root system has a main root that grows down vertically, and from which many smaller lateral roots arise. Dandelions are a good example; their tap roots usually break off when trying to pull these weeds.
5.3 Inside Roots The Science of Plants
Zea mays. Zea mays (corn) is often used as a model organism for monocot anatomy. Figure 11.1.2.1 11.1.2. 1: The images above show a corn seedling in two different stages of development. The first image is of the corn seedling at an earlier stage. It has produced a shoot (with one cotyledon) and a long root (radicle).
class on structure of monocot stem YouTube
Monocot roots, also known as monocotyledonous roots, are a crucial part of the root system in plants belonging to the monocotyledonous group. Monocotyledonous plants, or monocots, are a class of flowering plants that have a single cotyledon or seed leaf in their embryonic stage.
11.1.2 Monocot Roots Biology LibreTexts
Category: Animals & Nature Byname: monocot Key People: Agnes Arber Related Topics: Asparagales Alismatales Pandanales Liliales Petrosaviales See all related content → monocotyledon, one of the two great groups of flowering plants, or angiosperms, the other being the eudicotyledons (eudicots).
Monocot vs. Dicot Root Differences and Similarities
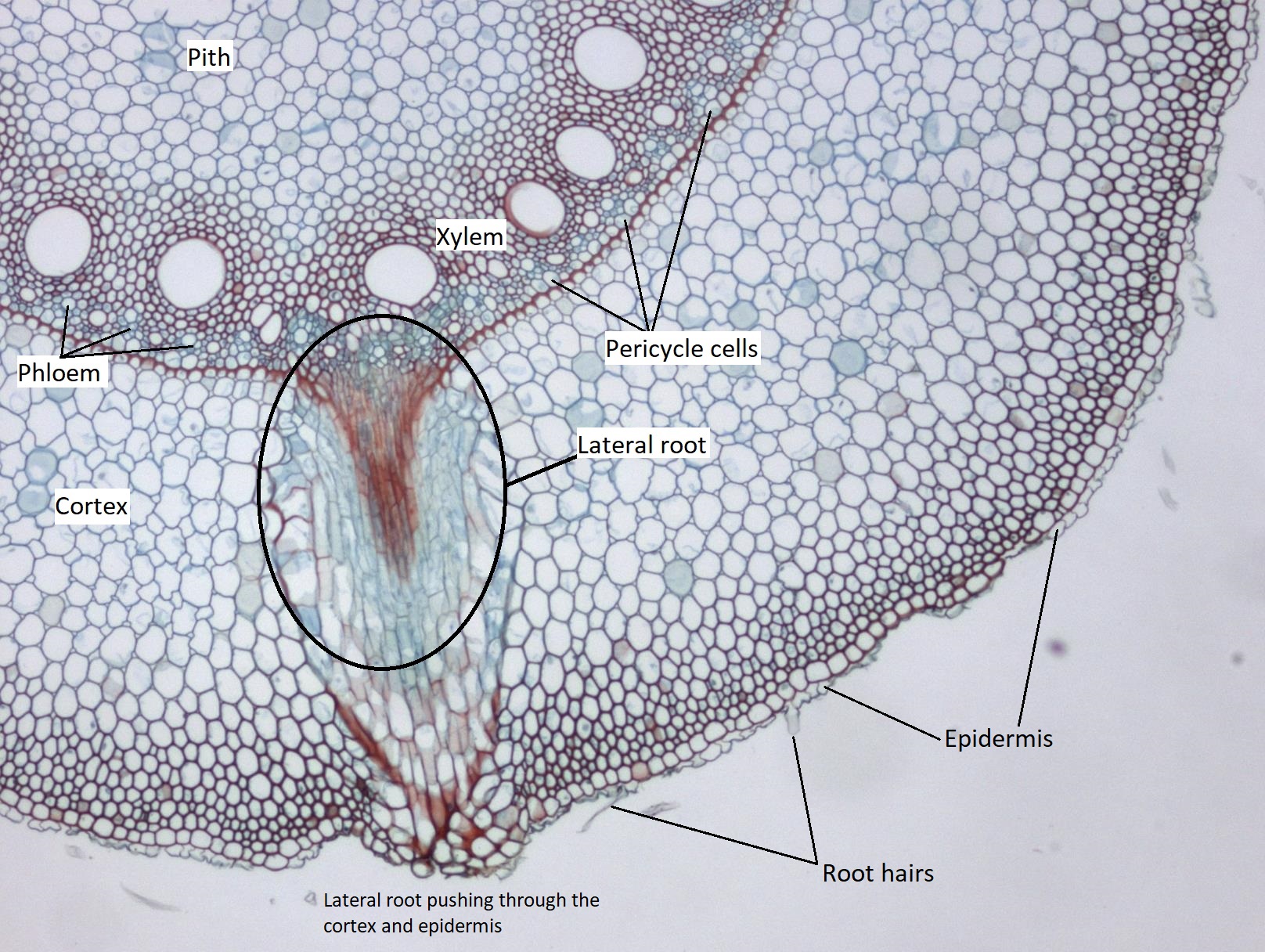
Monocot Root Diagram. (4). Pericycle. Ø The layer (s) of cells occupying between the endodermis and vascular tissue is called pericycle. Ø Usually, the pericycle composed of a single layer of thin walled parenchymatous cells. Ø In Smilax, the pericycle is multiseriate and thick walled.
Monocot Root Vascular Arrangement Photograph by Steve Gschmeissner
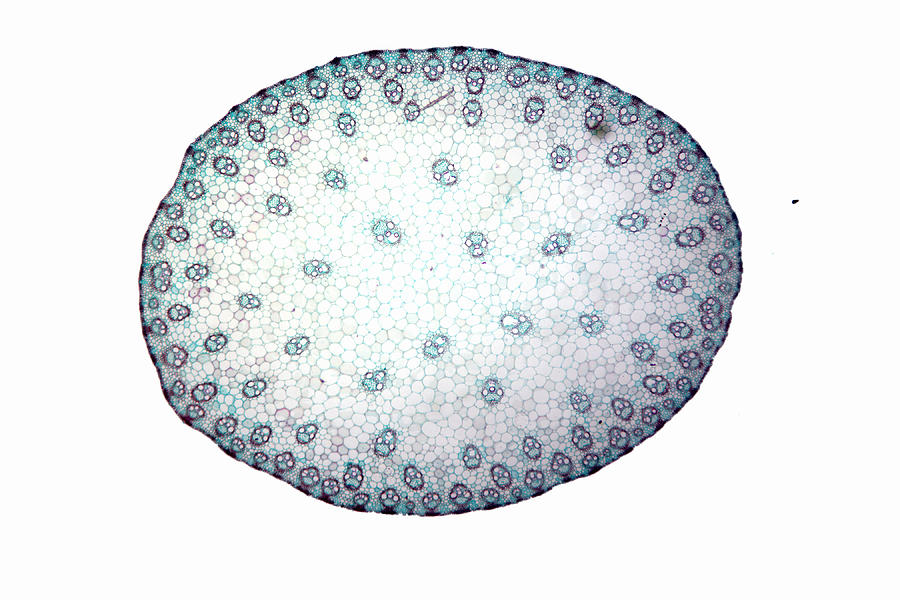
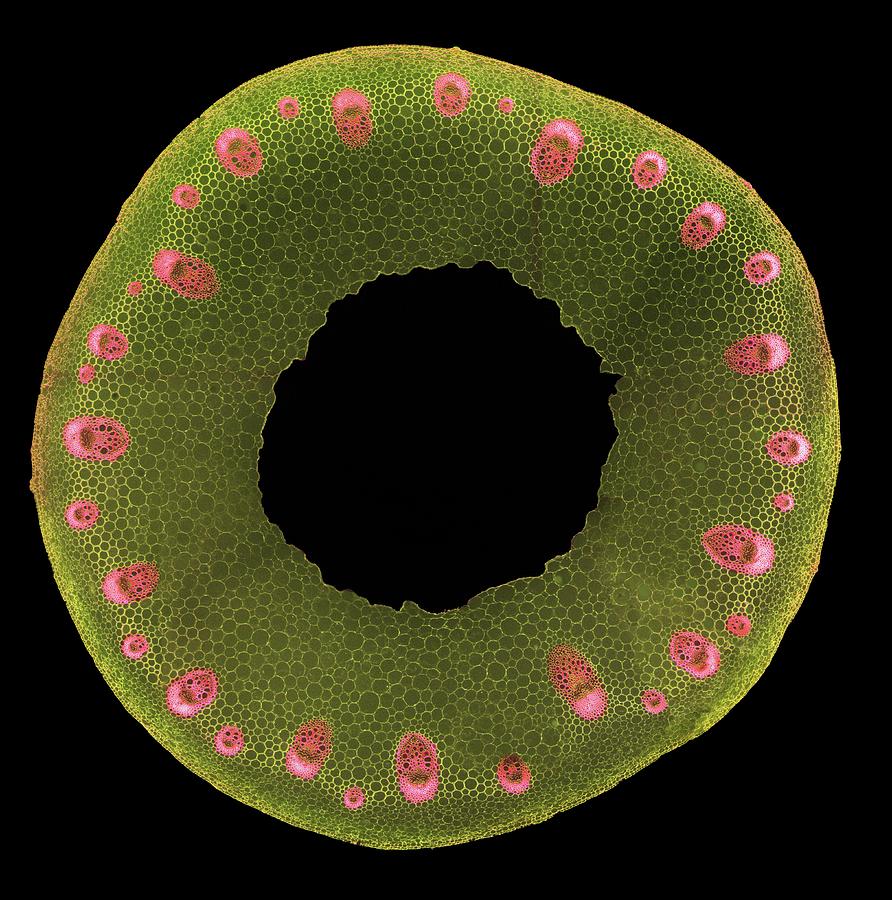
Monocot root. Monocot roots have a fibrous structure, meaning they form a wide network of thin roots that originate from the stem and stay close to the soil surface. The ground tissue of monocot roots, primarily composed of parenchyma cells, is divided by a ring of vascular tissue into the outer cortex and central pith. See it in 3D! Epidermis

Monocot Root Cross Section BryannatuCaldwell
Monocotyledons ( / ˌmɒnəˌkɒtəˈliːdənz / ), [d] [13] [14] commonly referred to as monocots, ( Lilianae sensu Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon.

PPT Chapter 6 Roots PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5564945
1. Monocot and dicot roots have very different appearances. Before we look at the structures and tissues inside monocot and dicot roots, let's examine how their overall shape and structure differs. Monocot roots are fibrous, meaning they form a wide network of thin roots that originate from the stem and stay close to the surface of the soil.
Monocot Root Vascular Arrangement Photograph by Steve Gschmeissner
8.4: Monocots. Monocots are a group of flowering plants that produce a single first leaf ( cotyledon) as their seeds germinate. Eudicots (frequently referred to simply as dicots) produce two cotyledons. In addition to this feature, monocots and eudicots can be distinguished by several anatomical and morphological features.

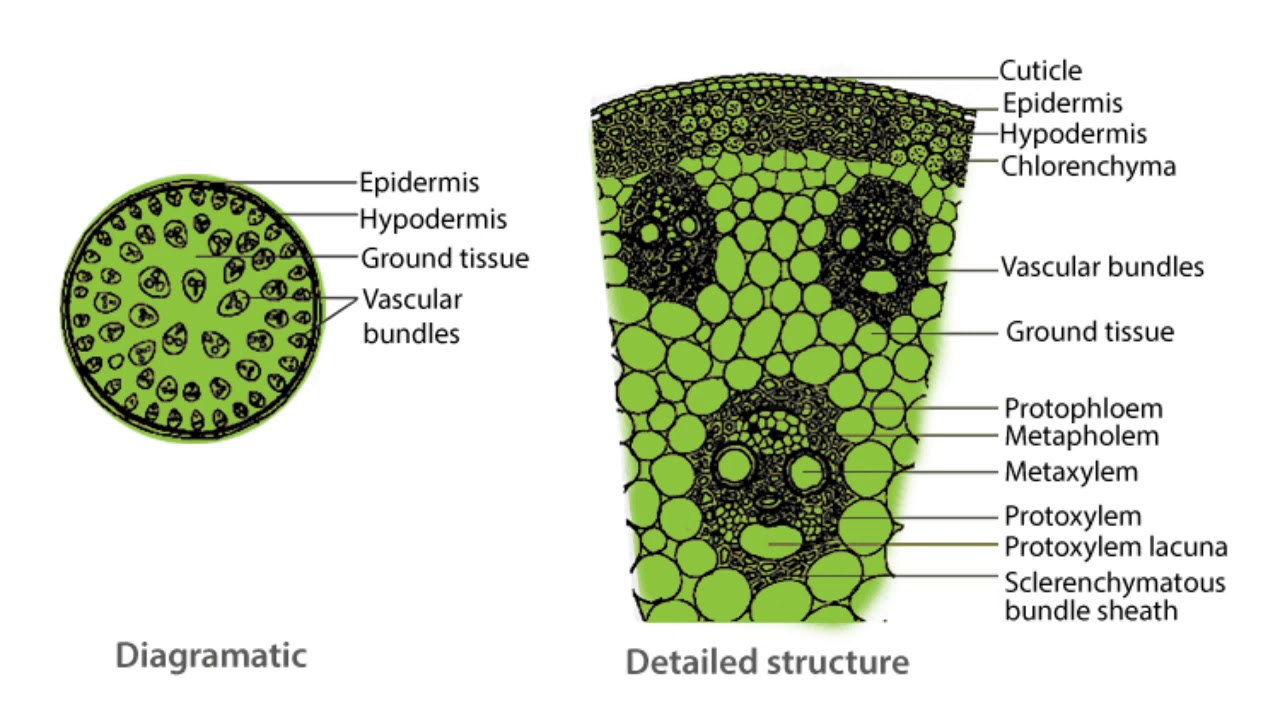
Internal Structure of Monocot Stem Notes Free Biology Notes Rajus
Definition of Monocot Root Definition of Dicot Root Read Also: Monocot and Dicot Leaves- Definitions, Structure, 13 Differences, Examples Structure of Monocot and Dicot Root 1. Piliferous Layer or Epiblema or Epidermis 2. Cortex 3. Endodermis 4. Pericycle 5. Vascular Bundles 6. Conjunctive tissues 7. Pith 8. Passage Cells
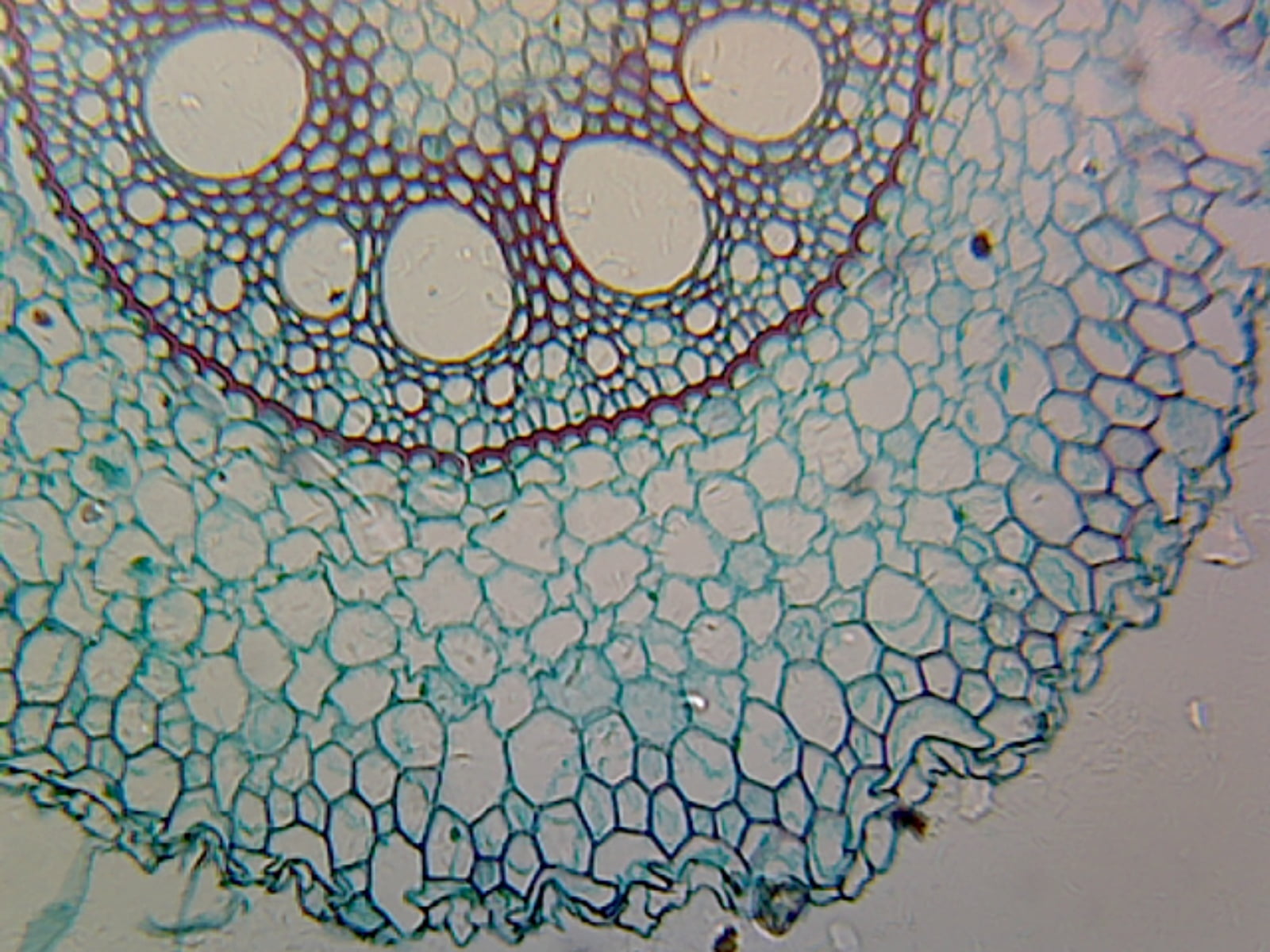
Angiosperm Root; Monocot; Showing General Structures; Cross Section
Monocot Roots Those plants whose seed contains only one cotyledon is known as monocot plant (or monocotyledon). In this tutorial, you will learn about the characteristics and anatomy of monocot roots. Primary Structure of Monocot roots The typical monocot roots show the following features:

monocot stem anatomy
Roots The roots of monocots cannot grow in diameter due to the lack of vascular cambium. Instead, they grow more roots at the shoot (radicle) and send out creeping shoots called runners or rhizomes (Figure 1). The coleorhiza is a tough sheath of tissue at the end of each root that protects it as it works its way through the soil.
