
Glucose Structure, Properties, Synthesis, Facts & Summary
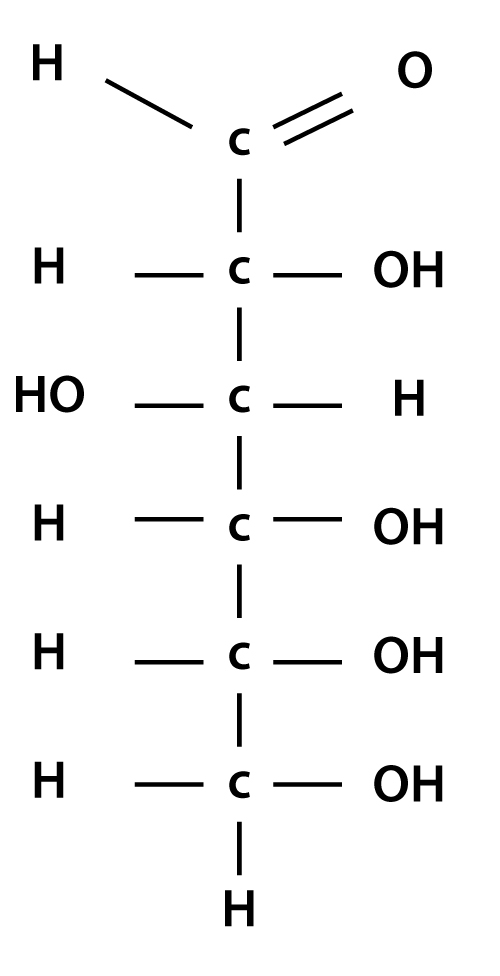
Steps to Draw Open Chain Structure of a Glucose Molecule Follow the steps given below to draw an acyclic form of glucose. Step 1: Draw 6 carbon atoms Step 2: Draw extended arms for all the carbon atoms excluding the first one. Step 3: Now draw hydrogen to carbon bond such that four are on one side and one on the other side.

Structural chemical formula and model glucose Vector Image
21: Carbohydrates 21.4: Structure of Glucose and Other Monosaccharides

Basics of Carbohydrates
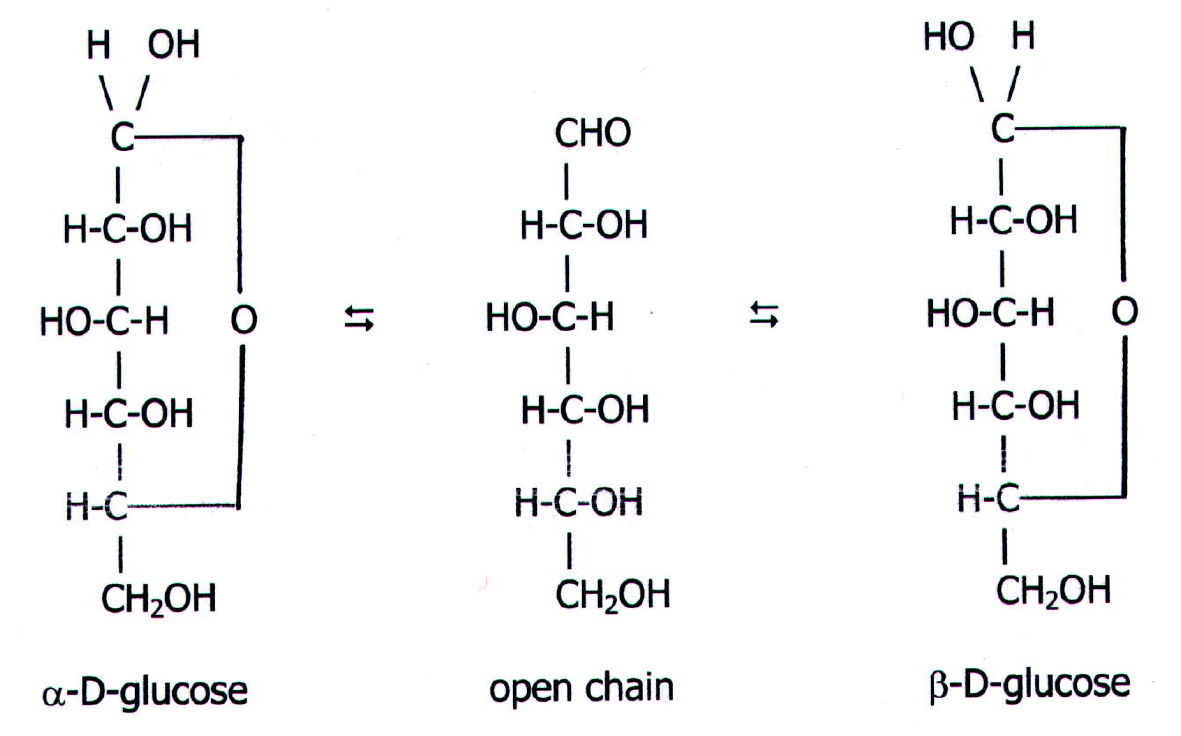
Learn to draw the open chain structure and ring structure in easy to follow steps. Note that there are in fact 3 versions of the ring structure. I have shown.
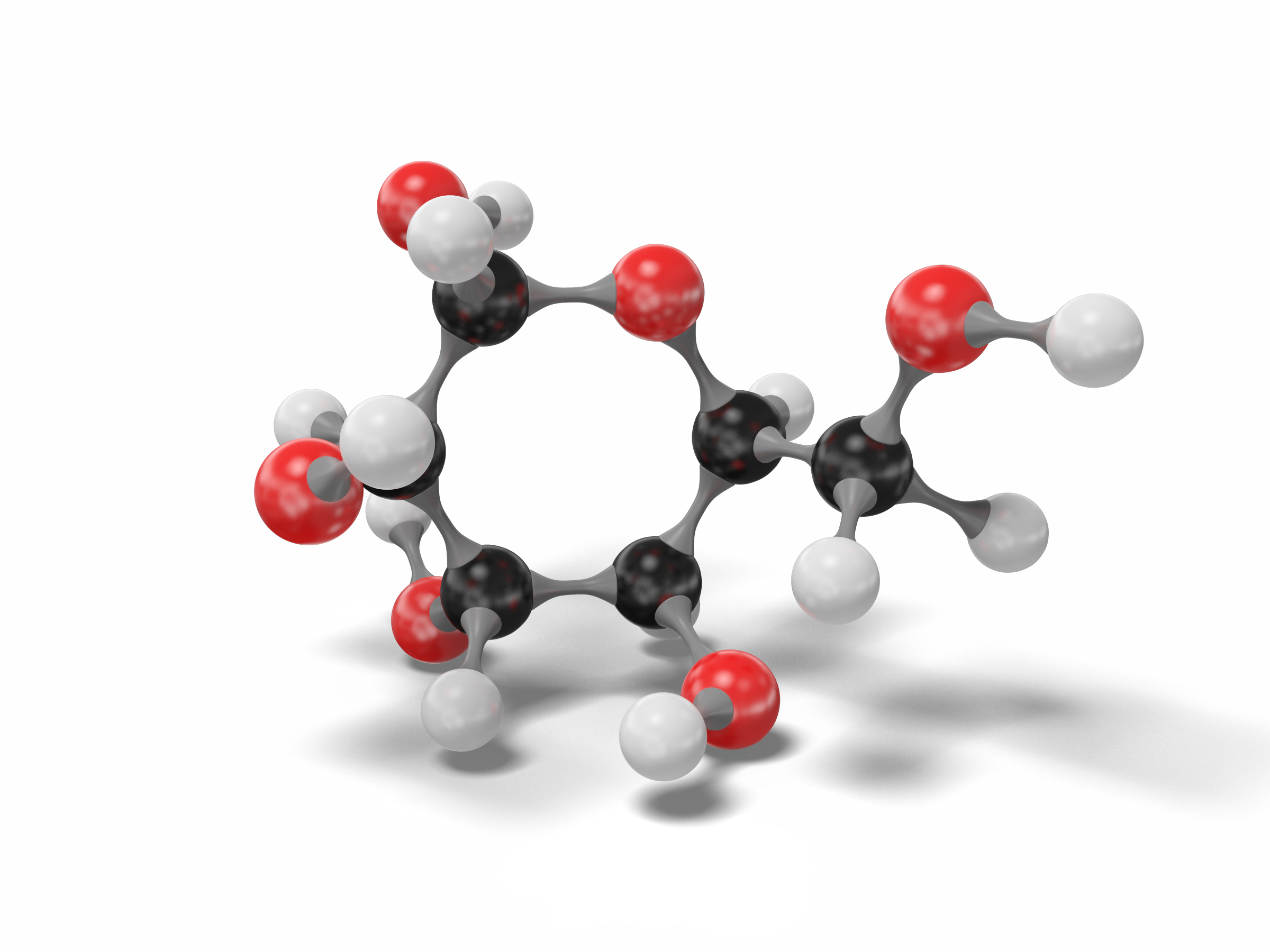
3D model glucose molecule modeled TurboSquid 1542502
Google Classroom Overview of carbohydrates, including structure and properties of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Introduction What's in a spud? Besides water, which makes up most of the potato's weight, there's a little fat, a little protein…and a whole lot of carbohydrate (about 37 grams in a medium potato).

Classification of Carbohydrates with Types, Formula and Structure
Glucose is a 6-carbon structure with the chemical formula C6H12O6. It is a ubiquitous source of energy for every organism in the world and is essential to fuel both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. Glucose often enters the body in isometric forms such as galactose and fructose (monosaccharides), lactose and sucrose (disaccharides), or starch (polysaccharide).
Solutions, Solubility, and Colligative Properties Chemistry Visionlearning
Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: the energy-requiring phase, above the dotted line in the image below, and the energy-releasing phase, below the dotted line. Energy-requiring phase. In this phase, the starting molecule of glucose gets rearranged, and two phosphate groups are.
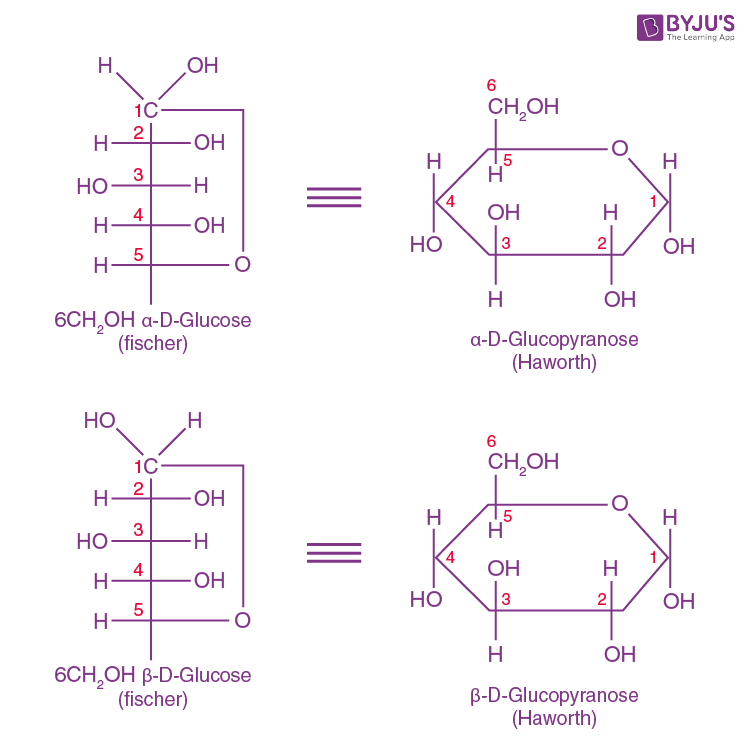
Glucose Structure Diagrams, Examples, Physical Properties
Summary. Glucose is the most important monosaccharide that provides energy to cells present in our bodies. It is an aldohexose having an aldehydic group and multiple hydroxyl groups attached to six carbon atoms. Its structure can be represented by an open-chain structure or a closed ring. Glucose has 16 isomers.
4 simple steps to drawing chain structure of glucose molecule
Structure of glucose Carbohydrates are composed of naturally occurring organic compounds of carbon-hydrogen and oxygen, which are primarily produced by plants. Carbohydrates are formed by plants by a process known as photosynthesis. The general formula of carbohydrates is Cm (H2O)n

Glucose structure and function Zogor
Historically, carbohydrates were defined as substances with the empirical formula C n (H 2 O) m.The common sugars such as glucose and fructose (n = m = 6), or sucrose (n = 12, m = 11) fit this formula, but nowadays the convention is to regard as a carbohydrate a polyhydroxyaldehyde or polyhydroxy ketone with the classical formula, a molecule closely related to it, or oligomers or polymers of.

Glucose 3D Model C6H12O6 3D model CGTrader
Open-Chain Formula of Glucose Structure The open-chain formula of glucose can be determined by considering the following facts: Molecular formula: The molecular formula, C 6 H 12 O 6, is established from the analysis of glucose's elements and its molecular weight.

stereochemistry Why is it important that glucose’s third OH group points to the left
To draw an open chain structure or acyclic structure of glucose, we need to follow these steps- Step I- Draw 6 carbon atoms bonded to each other by a single bond in a straight chain. Step II- Extend the remaining two bonds of four carbon atoms in the middle and attach hydrogen to one side of these carbon atoms.
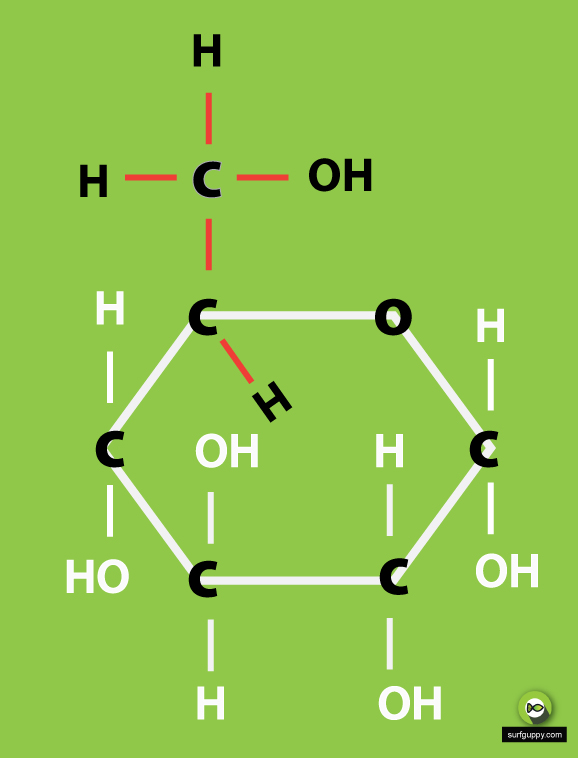
3 Simple Steps Draw the ring structure of glucose molecule
Molecular structure of glucose (video) | Khan Academy Biology library Course: Biology library > Unit 5 Lesson 2: Carbohydrates Molecular structure of glucose Dehydration synthesis or a condensation reaction Hydrolysis Molecular structure of fructose Carbohydrates Carbohydrates Science > Biology library > Macromolecules > Carbohydrates
Glucose Chain Structure
In sucrose, a glycosidic linkage is formed between carbon 1 in glucose and carbon 2 in fructose. Common disaccharides include lactose, maltose, and sucrose (Figure 3.2.5 3.2. 5 ). Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of the monomers glucose and galactose. It is found naturally in milk.

What is Biomolecules Definition of Biomolecules, Notes, Examples, Books
Chemical and physical properties Glucose forms white or colorless solids that are highly soluble in water and acetic acid but poorly soluble in methanol and ethanol.
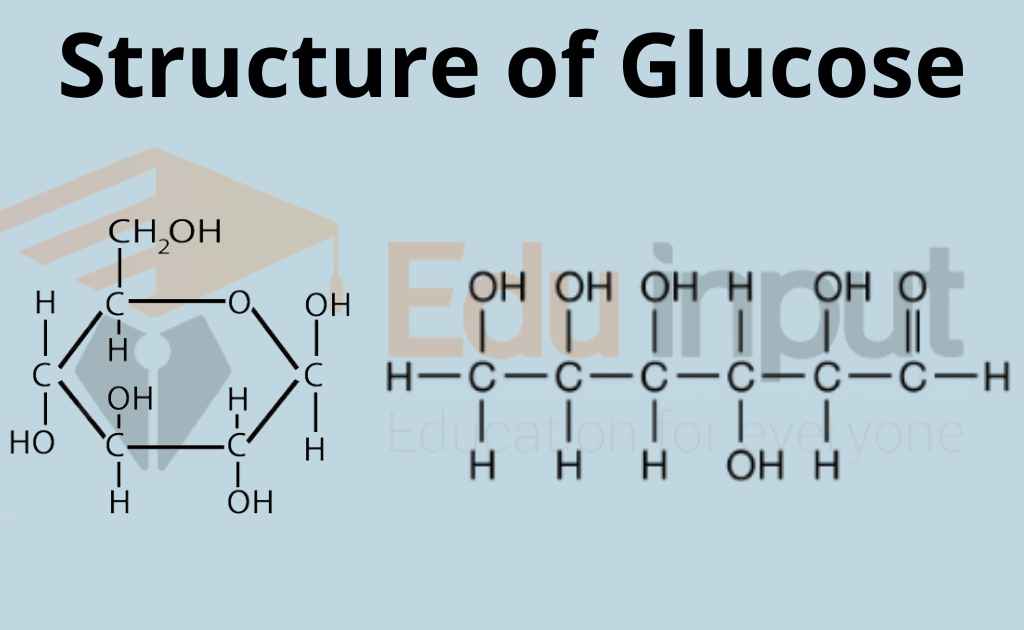
What is Glucose?Glucose in Plants, Animals, and Humans
Configuration. Glucose is by far the most abundant monosaccharide; it occurs free in fruits, plants, honey, in the blood of animals, and combined in many glycosides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. The structure and properties of glucose will be considered in greater detail than those of the other monosaccharides, not only because of its.

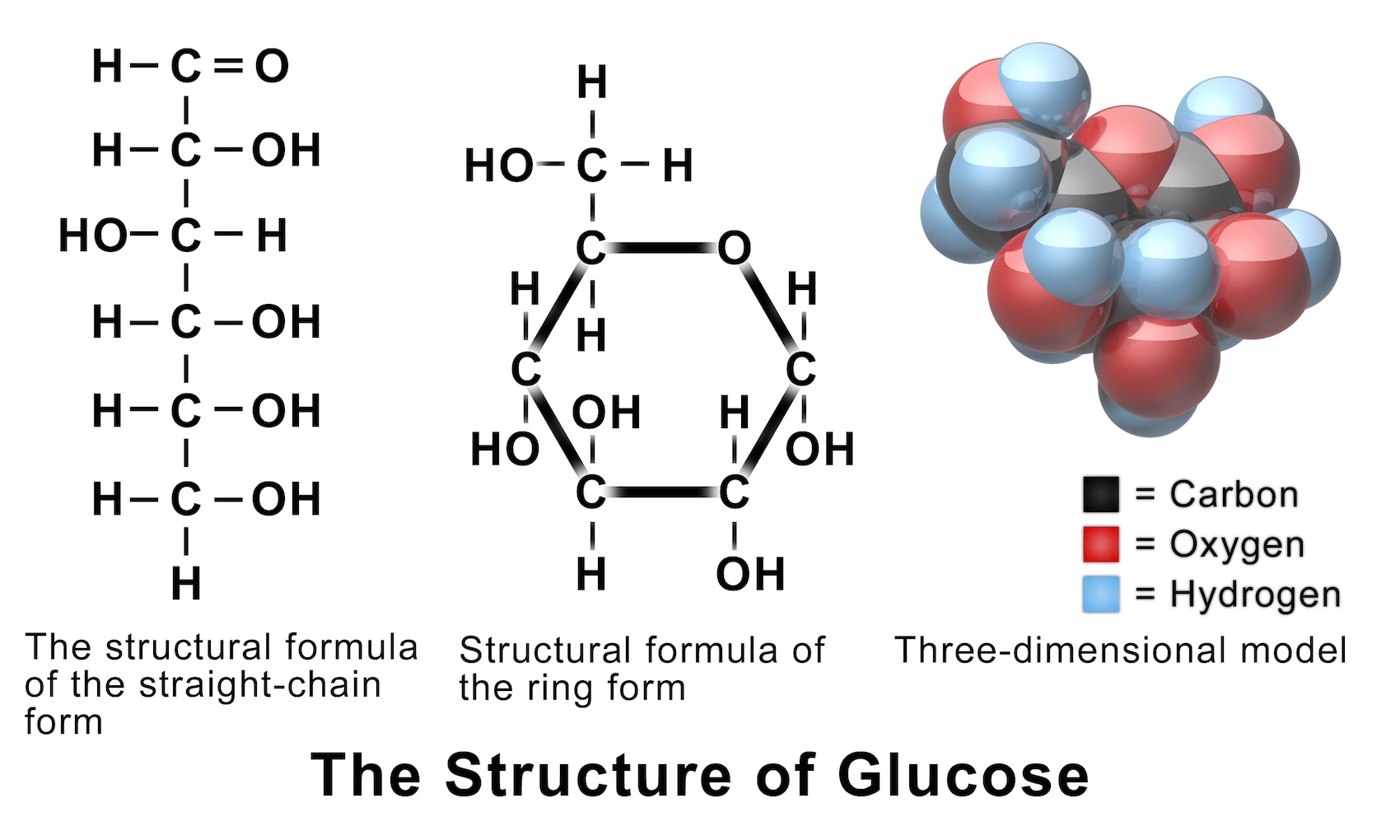
The Structure of Glucose Structural formula, Pearson education, Anatomy and physiology
Figure 8.2.1:Glucose and fructose are monosaccharides, or simple sugars. Glucose and fructose are both soluble in water. In aqueous solution, the predominant forms are not the straight-chain structure shown above. Rather, they adopt a cyclic structure (see figure below). Glucose is six membered ring, while fructose is a five-membered ring.
